Version and amend data structures
Every data structure is based on a versioned schema.
There are two kinds of schema changes:
- Non-breaking - a non-breaking change is backward compatible with historical data and increments the
patchnumber i.e.1-0-0->1-0-1, or the middle digit i.e.1-0-0->1-1-0. - Breaking - a breaking change is not backwards compatible with historical data and increments the
modelnumber i.e.1-0-0->2-0-0.
Different data warehouses handle schema evolution slightly differently. Use the table below as a guide for incrementing the schema version appropriately.
| Redshift | Snowflake, BigQuery, Databricks | |
|---|---|---|
| Add / remove / rename an optional field | Non-breaking | Non-breaking |
| Add / remove / rename a required field | Breaking | Breaking |
| Change a field from optional to required | Breaking | Breaking |
| Change a field from required to optional | Breaking | Non-breaking |
| Change the type of an existing field | Breaking | Breaking |
| Change the size of an existing field | Non-breaking | Non-breaking |
In Redshift and Databricks, changing size may also mean type change. For example, changing the maximum integer from 30000 to 100000. See our documentation on how schemas translate to database types.
Automatic versioning with the data structure builder
Versioning is automated when using the data structure builder to create or edit your custom data structures.
It will automatically select how to version up your data structure depending on the changes you have just made.
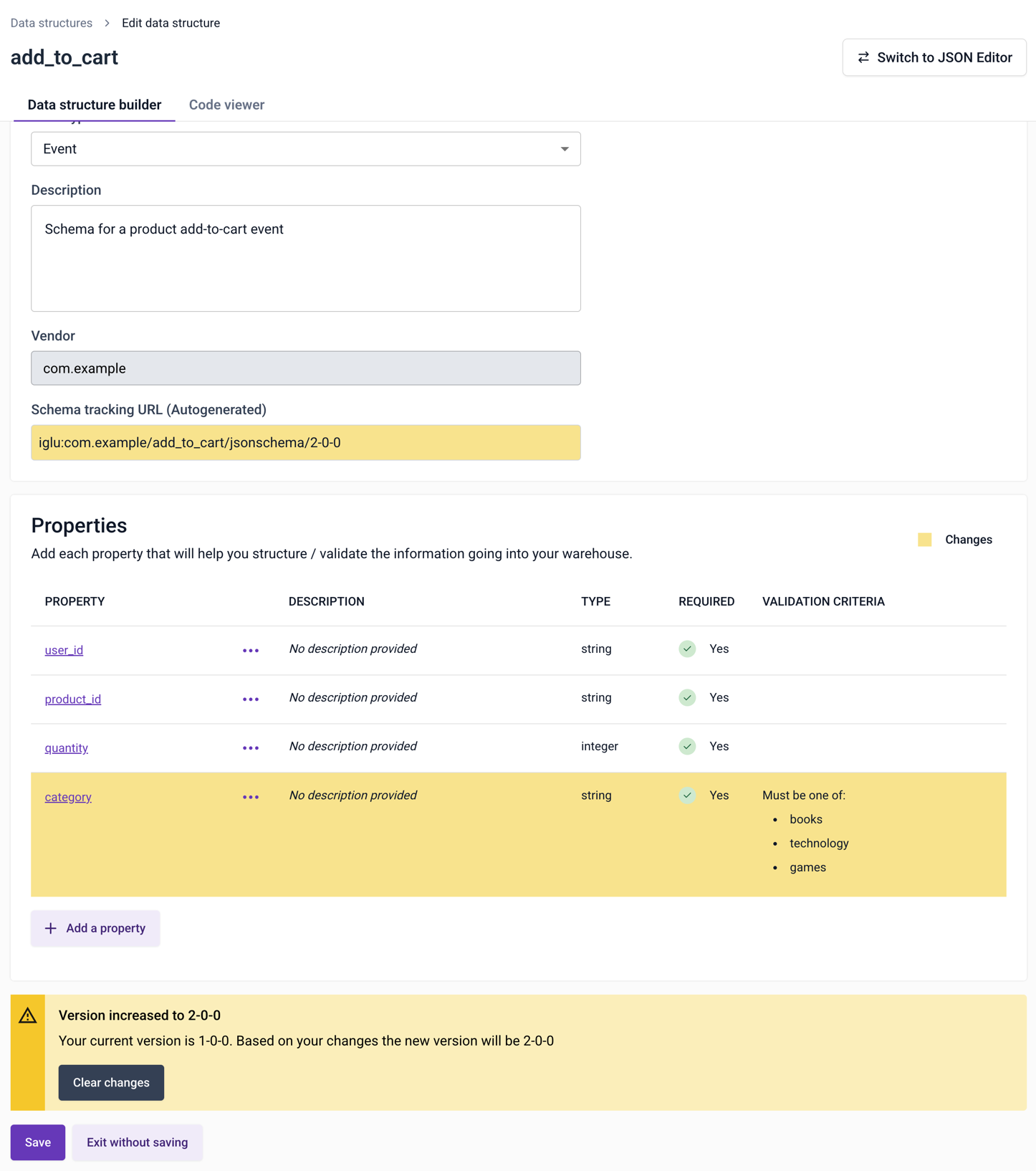
In this example, a new required property has been added to the data structure. This is a breaking change, so the builder will increment the first digit:
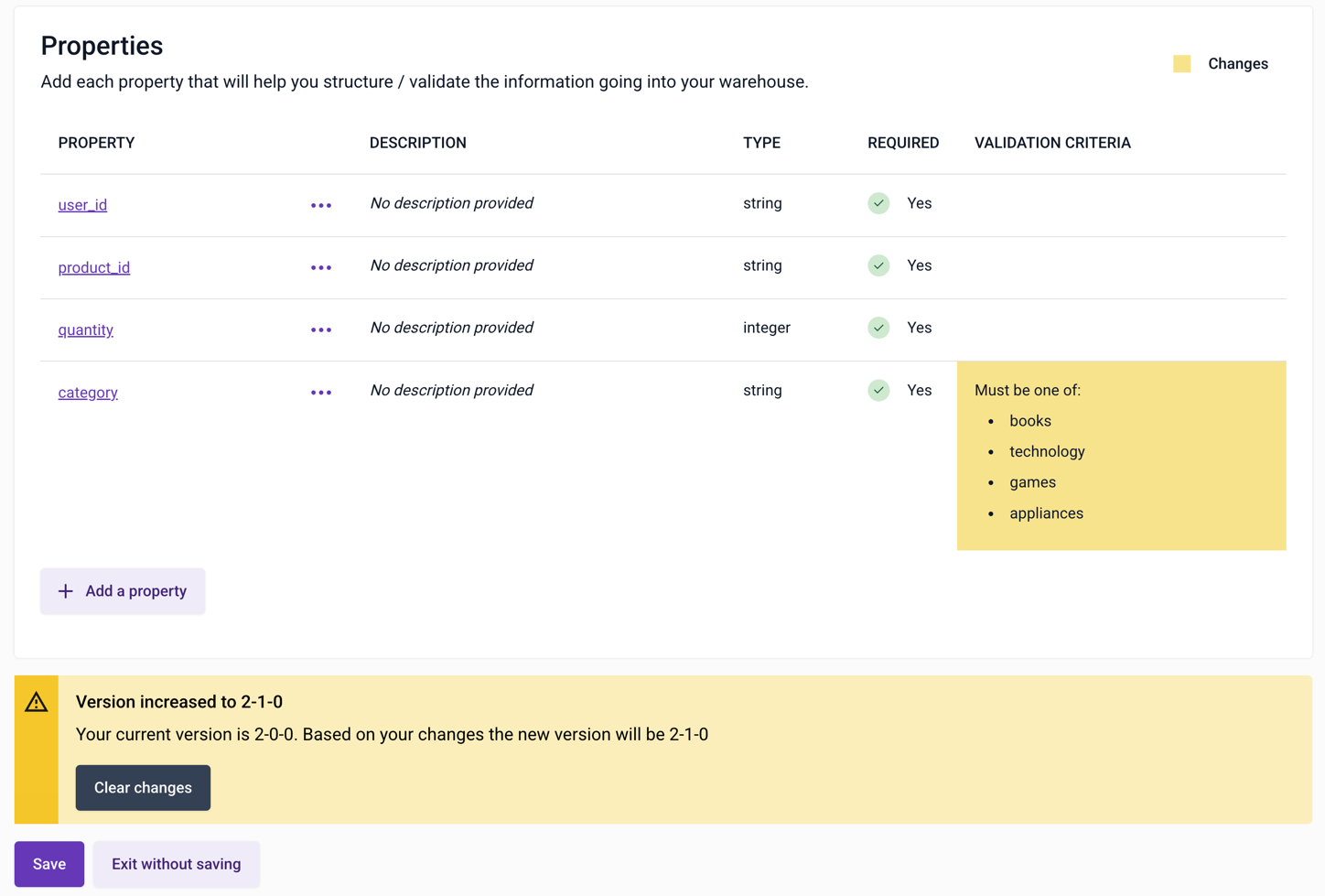
In this example, an additional enum option has been added to category. This is a non-breaking change, so the builder is incrementing the middle digit:
Versioning with the JSON editor
When using the JSON editor, at the point of publishing a data structure you'll be asked to select which version you'd like to create.
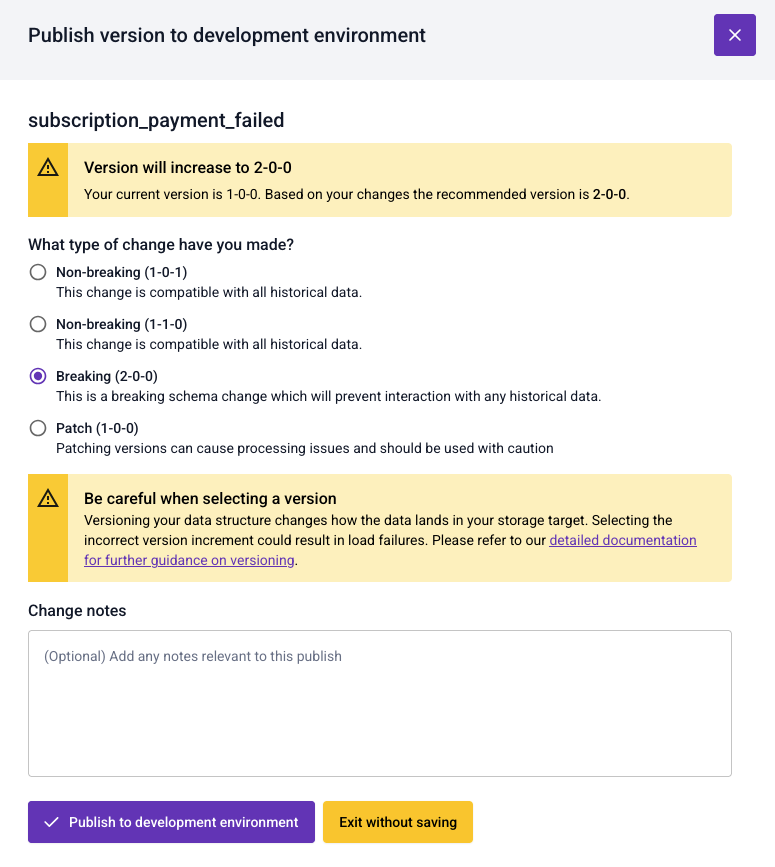
Patch a schema
To patch a schema, i.e. apply changes to it without updating the version, select the Patch option when saving the schema.
Note that various pipeline components, most importantly Enrich (including Enrich embedded in Snowplow Mini and Snowplow Micro), cache schemas to improve performance. The default caching time is 10 minutes (it's controlled by the Iglu Resolver configuration). This means that the effect of patching a schema will not be immediate.
If you are using Snowplow Self-Hosted, to patch a schema, don't increment the schema version when uploading it with igluctl.
You'll need to explicitly enable patching in the Iglu Server configuration (patchesAllowed) at your own risk.
Mark a schema as superseded
To mark a schema as superseded, use the JSON editor and add a $supersedes field.